Discover:
- What are merchant services?
- How do merchant service providers work?
- What equipment or technology do you need for merchant services, and who provides it?
- What is a merchant account?
- How did merchant services start?
- What are the benefits of having a merchant account with a merchant service provider?
- How to evaluate a merchant service provider
- How to get started with Amazon Pay merchant services
What are merchant services?
“Merchant services” is the overall term that refers to a suite of financial services for businesses. These include credit card processing, facilitating the acceptance of payments, access to payment technology, lending, and shortening the time from customer transactions to cash deposits in businesses’ accounts.
The term “merchant services” is often used interchangeably with “payment processing” and “credit card processing,” but there are some key differences. These are all systems that handle financial transactions from customers, but merchant services can include more than that. Many businesses use merchant service providers not only to enable electronic transactions but also to enhance their checkout capabilities and expand their payment options.
Who qualifies as a merchant and who uses merchant services
Any person or company that sells goods or services qualifies as a merchant. And most merchants can benefit from merchant services.
These are the types of businesses that typically use merchant account partners:
Ecommerce merchants:
Ecommerce merchants are online-only businesses, sometimes called “click-and-mortar” businesses, that sell to shoppers exclusively via the internet. They integrate merchant services with their existing business technology through secure apps and browsers to sell via desktop and mobile devices.
Retail merchants:
A retail merchant is a business that sells goods or services to the public. Retail merchants can include online-only businesses as well as brick-and-mortar stores with a physical location a shopper can visit in person.
Wholesale merchants:
Wholesale merchants buy products from manufacturers (or other wholesalers) and then resell them to retail merchants, government agencies, or other businesses.
Affiliate merchants:
Affiliate merchants, or associate merchants, include influencers, bloggers, and publishers who choose to include links to products or services sold by a third-party ecommerce retailer. The products are often presented as recommendations from the content creator to help them monetize their web traffic via a commission for a referral.
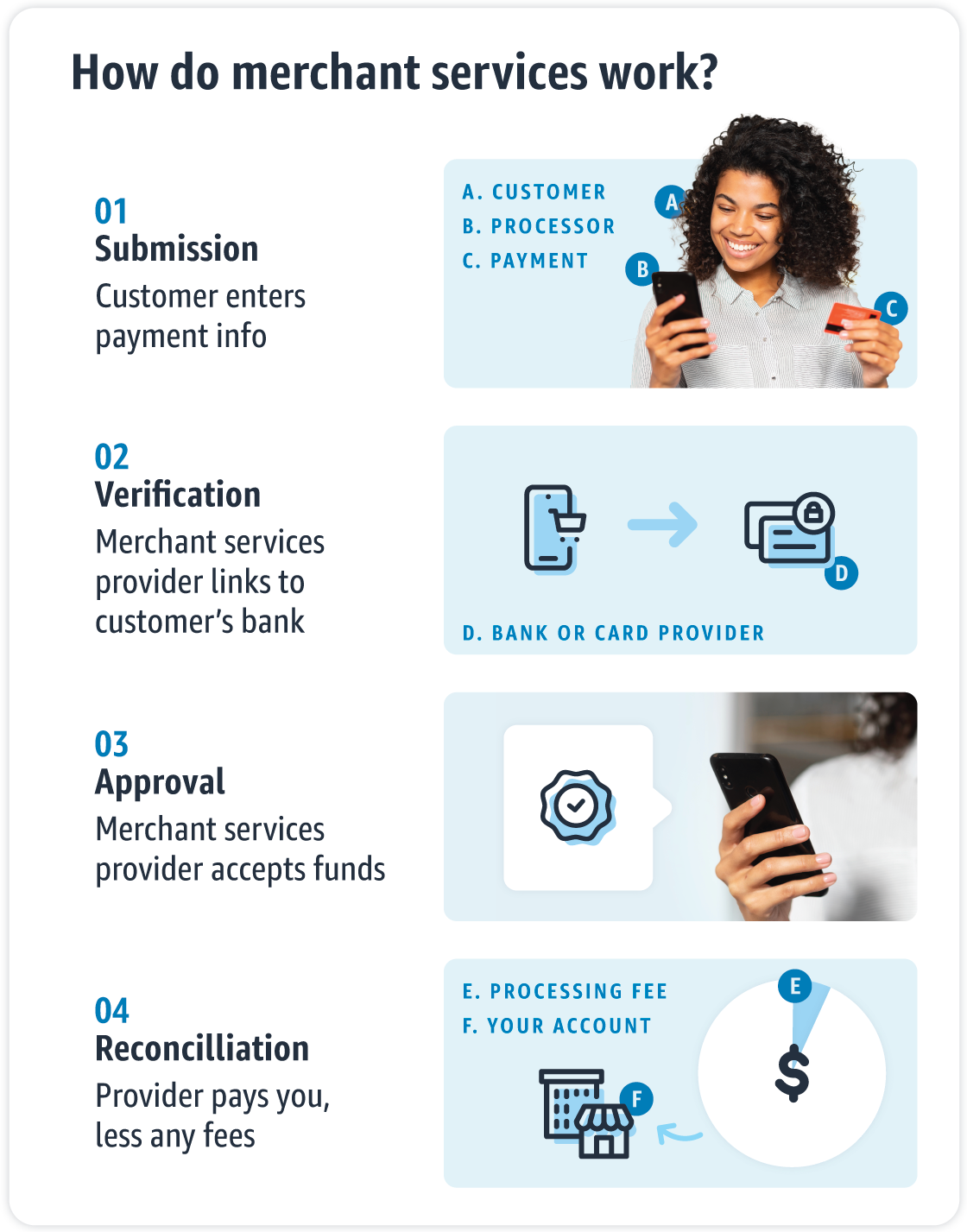
How do merchant service providers work?
Merchant service providers take over when a customer hands their credit card to a business until the revenue is deposited in the merchant’s account.
1. The customer enters payment information into a credit card processing terminal.
2. The merchant service provider transmits this data to the customer’s bank to accept or decline.
3. Once the charge is approved, the merchant accepts the payment and the purchase is complete.
4. The merchant service provider takes its fees and deposits the remaining funds into the merchant’s account.
What equipment or technology do you need for merchant services, and who provides it?
Businesses use merchant services to cut out unnecessary equipment, technology, or processes. Merchant service providers help streamline operations to handle payments more efficiently, so your merchant service provider supplies the transacting system. As new technology evolves, providers let you expand easily by offering more payment options without increasing costs.
Merchant Services for Ecommerce
Merchant payment gateways: Merchant payment gateways are the building blocks of ecommerce transactions. They are digital point-of-sale (POS) terminals that are necessary to accept card-not-present (CNP) transactions. During digital transactions, the credit card information is submitted online rather than face-to-face. Merchant payment gateways act as verification to send credit card data and communicate declines and approvals.
Merchant Services for Brick-and-mortar
POS systems:
POS systems are designed for in-person payment transactions. Merchant services often include payment terminals. The three most common kinds of POS systems are:
Terminal systems: The tech-enabled hardware you think of when you think of in-person payments. For example, cash registers with barcode scanners, card readers, PIN pads, etc.
Mobile POS systems: App-based processors that connect to the merchant’s own equipment via a smartphone or tablet.
Online POS systems: These require a card reader for transactions but allow merchants to use their own equipment, like a tablet or PC.
Credit card terminals:
Contactless payments: Contactless payments are at the forefront of in-person shopping technology. Customers simply tap their contactless card or payment-enabled device to a contactless-enabled payment terminal. Cards, phones, watches, and other devices all use similar contactless technology.
Mobile payments: Mobile payments include browser-based payments and in-app purchases accessed from a mobile device. When paying on mobile, customers can check out with the information stored in their device’s digital wallets.
Virtual terminals:
A virtual terminal is an application that allows a retailer to accept payments from a customer’s credit card without the physical presence of the card. Before approving a CNP transaction, to verify a customer has the physical card they are attempting to use, the virtual terminal will often require the customer to enter the credit card’s security code. Virtual terminals are an attractive option for many stores as they provide merchants the flexibility to choose the device they want to use for transactions, including computers, tablets, and mobile phones.
What is a merchant account?
A merchant account is the account made available to you by the service provider where information about payment transactions is collected and where funds are held to be transferred as transactions clear.
Online transaction processing (OLTP) enables the real-time processing of online payments. Every transaction you make is sorted through online databases to deliver your information and process your requests.
Do you need a merchant account?
Yes. If you conduct traditional commerce or ecommerce, you will almost certainly need a merchant account. All merchants that accept credit cards have a merchant account in one way or another.
What are ACH payments?
Automated clearing house (ACH) payments are a type of bank-to-bank payment made directly between accounts, rather than through card networks like Visa or Mastercard. Instead of paying with card information, for example, money is transferred using account and routing numbers. These include direct deposits or direct payments.
Processing ACH payments is often much cheaper than using card payments because they often carry lower fees. Fees vary depending on the transaction. However, typically businesses with larger transaction volumes pay less per transaction. This is beneficial for merchant accounts, which often operate through ACH payments.
How did merchant services start?
What are the origins of merchant services?
Merchant services have evolved over the past decades to serve the needs of businesses and consumers alike. From the first electronic payment transactions to the rapidly changing industry we know now, merchant services still exist to improve the shopping experience.
Since the inception of ecommerce, there has been a boom in electronic transactions. This industry shift emphasized the need for new, expanded merchant service offerings.
Now, the merchant services industry is full of providers all offering businesses new ways to improve their flow, decrease their overhead, and increase their profits. And to keep up with customer demand, they’re always offering new updates and innovations to help serve their business partners best.
What are recent evolutions in merchant services?
Merchant service providers are responsible not only for carrying out transactions, but also for bringing payment evolutions to their partners. The recent acceleration of ecommerce has meant big updates in global payments as more businesses pivot to ecommerce.
In response, merchant service providers have seen an increase in demand. For many businesses, more customers mean more problems — greater risk of fraud, chargebacks, and quality of merchant security. To address their concerns, merchants are willing to pay a premium for high-quality merchant services.
What is the current state of merchant services?
To address the higher demand for merchant services, providers are seeking to differentiate themselves. To distinguish the best provider for their needs, businesses need to consider how to integrate newer solutions with their existing systems.
When a merchant service provider is a good fit, merchants can expect their service partner to:
1. Leverage the latest technologies
2. Integrate with existing systems easily
3. Streamline payments for shoppers
4. Provide dedicated technical support
5. Help grow their customer base
6. Accept multiple payment types
7. Reduce chargebacks and fraudulent transactions
8. … and be a recognized and trusted provider in the payment sector.
What is the future of merchant services?
Shoppers are always seeking faster and easier experiences. Therefore, merchants are, too. Merchant service providers on the cutting edge are exploring innovations like one-click payments, e-wallets on mobile/wearable devices, cryptocurrencies, merchant services for nonprofits, gift cards and loyalty programs, and touchless, autonomous retail.
What are the benefits of having a merchant account with a merchant service provider?
There are many benefits of working with a merchant service provider. These benefits are slightly different for small businesses and enterprise-scale operations.
Why should a small business work with a merchant service provider?
As your company grows, the business operations become more intricate. The retail landscape is constantly shifting. Customers expect the fastest, easiest, and best — especially when it comes to checkout. These days, integrate payment solutions via a merchant service provider is the best way for small- to medium-sized businesses to optimize their systems without increasing costs and effort. Merchant account partners help facilitate transactions in a merchant account, allow merchants to access their revenue faster, and help lower costs.
For small- and medium-sized businesses, the benefits of working with merchant service providers include:
A. Increased security and protection from fraud, chargebacks, etc.
B. A higher standard of merchant security standards
C. Ensuring secure transactions are PCI-compliant and providing basic consumer protections
D. Easy integration of CRM systems, data, analytics, and other business tools for increasing revenue
E. Lower operational costs, so you can free up resources to use elsewhere
F. Increased revenue from increased audience reach and faster operations
G. Simplified global capabilities with merchant services for international payments
H. And more
Why should enterprise businesses work with a merchant service provider?
Larger organizations carry all the benefits of scale, but there are downsides to handling transactions internally. Larger operations mean more time invested by internal teams — and more room for error. By working with merchant service providers, you create efficiencies across the organization and limit reliance on personnel.
The benefits of working with merchant service providers for enterprise-level businesses include:
I. Increased security and protection from fraud, chargebacks, etc.
J. Compliance to merchant service security standards
K. Flexibility to accept multiple payment methods and update with new technology
L. Enterprise-level capacity to consolidate payments into the business’s sales stack with CRM and other integrations
M. Lower operational costs through reduced reliance on personnel
N. Increased revenue from increased audience reach and faster operations
O. And more
How to evaluate a merchant service provider
Merchant service providers for small- to medium-sized businesses
Choosing the right merchant service provider is the key to unlocking all the benefits for your business. Most merchant payment partners provide similar services, but the small differences can help you find the one tailored to your needs.
For small to medium businesses, here are questions to consider in a merchant payment partner.
What does it cost?
1. What are the associated fees? Consider what the fees are per transaction, as well as what it costs to get started. Are there start-up fees? And do your customers have to pay fees, too? Are there fees for international transactions? Investigate all the potential costs to calculate what you’re really paying.
2. Is it a flat rate or tiered? Some providers charge a flat rate, while others require a monthly subscription or a tiered service depending on what capabilities you need.
What kinds of payments are you accepting?
Cash? Credit? Crypto? Your choice of merchant providers will depend on which payment methods your customers use. Make sure your merchant services provider accepts them.
Are you mostly transacting online or in person?
Many small and medium businesses are online only, with an ecommerce site as the main destination for shoppers. Online-only click-and-mortar stores often just need a third-party provider to process their payments at checkout. If this is the case, you should choose an expert in ecommerce that prioritizes growth and optimization tools you can implement into your design.
Businesses with both online and offline locations should consider a provider that is able to provide and support countertop POS terminals, mobile POS terminals, or virtual terminals as well as online checkouts. Merchant service providers for this type of business need to be versatile and flexible.
What kind of hardware do you need?
Merchant service providers usually handle most of the tech involved in the payment process. However, you might need hardware to accept the payment in the first place. Many providers offer a range of hardware for in-person checkouts. Depending on your type of business, check what type of hardware your potential provider offers.
What kind of support do you need?
Businesses are only as good as the tools they’re able to use. That’s why knowing your provider is available to support you whenever you need can be mission-critical for sales.
Integrating merchant services with your ecommerce site should be an easy process, because not every business owner has a web development team ready to handle integrating payment processors. In addition to having access to extensive online technical resources for questions or technical issues, merchants should be able to contact the provider’s support team via email, phone, and/or chat whenever they are needed.
Learn more about what to look for when deciding on a merchant service provider for your business.
Merchant service providers for enterprise-level organizations
A. What is the merchant account pricing?
B. Do you receive benefits at scale?
C. What kinds of payments are you accepting?
D. What are competitors using?
E. Are you mostly transacting online or in person?
F. What kind of hardware do you need?
G. Do they offer enterprise-scale support?

How to get started with Amazon Pay merchant services
How Amazon Pay approaches merchant services
Is Amazon Pay trusted by top brands?
Top brands like Avis, Belkin, Crayola, Woot!, and hundreds of others have learned that with Amazon Pay, they can offer shoppers a trusted, convenient checkout experience with one familiar log-in to lower cart abandonment and optimize their customer experience.
Not only do top brands trust Amazon Pay but offering it on your site is an opportunity to benefit from one of the most trusted brands in the industry, ranked No. 3 in reputation by a 2020 Axios Harris Poll.
Does Amazon Pay have international capabilities?
Amazon Pay is available for established merchants in the United States, United Kingdom, Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Denmark, France, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland.Amazon Pay multi-currency capabilities make it easy for merchants to expand into new geographies and sell cross-borders. Shoppers can buy the products they love in their preferred currency, and businesses can receive funds into their bank accounts in the currency they prefer.
Does using Amazon Pay lead to faster checkout times?
Amazon Pay gives shoppers faster checkouts — 49% faster transactions than regular checkouts, according to a PYMNTS.com study.
If you use Amazon Pay, do your customers need to create new accounts?
Making a shopper create an account before buying an item they love can increase cart abandonments. Using the information already stored in their Amazon accounts, Amazon customers can pay on a business’s ecommerce site easily and without the added steps.
What are Amazon Pay’s fraud and prevention policies?
Shoppers can feel safe knowing that Amazon Pay is backed by the same fraud protection technology used on Amazon.com. With Amazon Pay, businesses can choose to process authorizations asynchronously, giving Amazon’s fraud models more time to analyze transactions for potential fraud. Learn about what ecommerce businesses can do to prevent fraud.
What is the Payment Protection Policy (PPP)?
The Payment Protection Policy may protect businesses from chargebacks, or charge disputes. If a transaction qualifies, Amazon Pay covers the chargeback with the required information. Learn more about the PPP by visiting Amazon Pay’s Chargeback FAQ.
What is the Amazon Pay A-to-z Guarantee?
Amazon has millions of satisfied customers and is always responsive to their concerns about a purchase. If a shopper isn’t satisfied with a purchase, they can file an Amazon Pay A-to-z Guarantee claim and potentially obtain full reimbursement for their purchase or cancel their authorized payment if they are not satisfied.
What IT support does Amazon pay offer?
Businesses that want to offer digital payments need a seamless integration experience. If a business uses a third-party ecommerce platform (like BigCommerce, Magento, and Woo), Amazon Pay integrates seamlessly with the solution provider so that adopting the payment service becomes plug-and-play. If a business has a custom-built website, it can rely on Amazon Pay to offer the technology and expertise to facilitate a seamless custom integration.




















